How can I lower my blood sugar naturally?
You can lower your blood sugar naturally by focusing on three core areas: diet, exercise, and sleep. Prioritize low-glycemic, high-fiber foods paired with protein, engage in regular physical activity like a 15-minute walk after meals, and ensure you get 7-9 hours of quality sleep per night. These actions improve your body's insulin sensitivity and help manage glucose levels effectively.
Managing your blood sugar without jumping straight to medication can feel empowering, but it can also feel a little overwhelming. This guide is built on a simple, real-world truth: small, consistent changes to your diet, movement, and daily routines have the biggest and most lasting impact. We're going to move beyond the generic "eat less sugar" advice and dig into the "why" behind each strategy.
We’ll cover everything from how to pair certain foods to prevent a glucose spike to the surprising power of a good night's sleep. We'll also look at how modern tools can take the guesswork out of nutrition, turning complex advice into a simple daily plan that helps you build a healthier lifestyle that actually sticks.
Why do small daily habits make such a big difference?
Many of the most effective strategies for blood sugar control are surprisingly simple and easy to weave into your daily life. They don't require a complete overhaul, but rather a series of mindful adjustments that add up over time. For instance, did you know that just getting more natural daylight can significantly improve blood sugar control for people with type 2 diabetes?
A groundbreaking study found that something as simple as sitting near a window during the day helps regulate insulin levels and how the body processes glucose. Participants who got more daylight exposure spent way more time within the healthy glucose range. It’s a perfect example of how small environmental shifts can play a huge role in your metabolic health.
Small, consistent actions are the foundation of long-term health. Instead of aiming for perfection, focus on making one better choice at a time—whether it’s choosing a whole-grain option, taking a short walk, or getting to bed 30 minutes earlier.
To provide a clear overview, this table summarizes the core strategies we'll be discussing. Think of it as your quick-reference guide to the most impactful actions you can take.
What are the key strategies for natural blood sugar management?
| Strategy Area | Key Action | Primary Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Dietary Choices | Prioritize fiber-rich carbs and pair them with protein/fat. | Slows glucose absorption, prevents blood sugar spikes. |
| Physical Activity | Engage in regular movement, like a walk after meals. | Improves insulin sensitivity and helps muscles use glucose. |
| Weight Management | Aim for a modest weight loss of 5-10% if overweight. | Significantly improves insulin resistance and blood sugar control. |
| Sleep Quality | Ensure 7-9 hours of consistent, quality sleep per night. | Regulates hormones that control appetite and blood sugar. |
| Stress Reduction | Practice mindfulness, deep breathing, or other techniques. | Lowers cortisol levels, which can raise blood sugar. |
| Hydration | Drink plenty of water throughout the day. | Helps kidneys flush out excess sugar through urine. |
Each of these areas contributes to a more stable and healthy metabolic state, demonstrating how a holistic approach is far more effective than focusing on just one or two habits.
How can I build a sustainable plan?
Trying to overhaul your entire lifestyle at once is a recipe for burnout. The real key to long-term success is to build healthy habits gradually, one on top of the other.
This is where planning tools can make a huge difference. For example, using an AI Meal Planner can take all the guesswork out of your nutrition. It generates personalized weekly meal plans and smart grocery lists tailored to your health goals. This simplifies the whole process, making it much easier to stick with a balanced diet without spending hours researching recipes and planning every meal.
The goal is to make healthy eating feel like an effortless part of your routine, not another source of stress.
What foods should I eat to stabilize my blood sugar?
Figuring out what to eat for better blood sugar control isn't about deprivation. It’s about being strategic. Think of it less like a restrictive diet and more like making smart, intentional choices that work with your body, not against it. It all starts with knowing how certain foods impact your glucose levels so you can build meals that keep you steady and energized, avoiding those jarring spikes and crashes.
A really helpful concept here is the glycemic index (GI). It's basically a ranking system for foods based on how quickly they make your blood sugar rise. Foods with a high GI—think white bread, sugary cereals, and pretzels—are digested fast, causing a rapid glucose surge. On the flip side, low-GI foods break down much more slowly, giving you a gradual, steady stream of energy.
How should I choose my carbohydrates?
Let's get one thing straight: not all carbs are villains. The trick is to focus on complex carbohydrates that are loaded with fiber. Why fiber? Because it slows everything down—digestion, and more importantly, the speed at which sugar enters your bloodstream.
Making a few simple swaps can have a massive impact. Instead of reaching for that plain white bagel for breakfast, try a slice of stone-ground whole-wheat or sourdough toast. These options have a lower GI and more fiber, which helps head off that sharp spike you might feel after a meal.
Here's a simple rule I tell my clients: the closer a food is to its natural, unprocessed state, the better it is for your blood sugar. A whole apple, with all its fiber intact, will always be a better choice than a glass of apple juice.
The infographic below really drives home how diet, exercise, and sleep are the three pillars of managing blood sugar naturally.
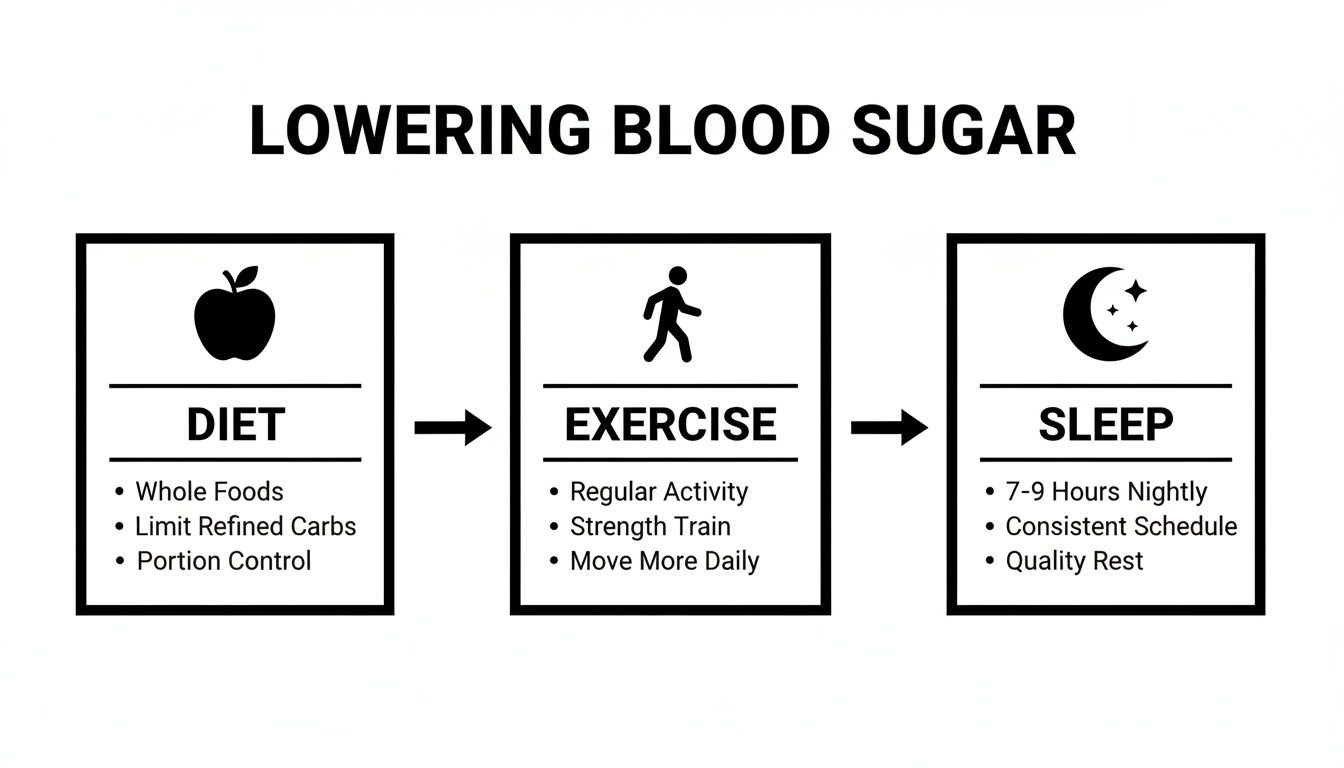
This visual is a great reminder that nutrition is just one piece of the puzzle. What you eat works in tandem with how you move and rest to create a healthy, balanced metabolic system.
To make this even more practical, here are some simple, powerful food swaps you can start making today.
What are some smart food swaps for better blood sugar control?
| Instead Of This (High-Glycemic) | Choose This (Low-Glycemic) | Why It Works |
|---|---|---|
| White Rice | Quinoa or Brown Rice | Both quinoa and brown rice are packed with fiber and protein, which slow down the absorption of sugar and keep you feeling full longer. |
| Sugary Breakfast Cereal | Rolled Oats with Berries and Nuts | Oats provide soluble fiber that forms a gel, blunting the sugar response. Berries add antioxidants and nuts provide healthy fats and protein. |
| White Bread or Bagels | 100% Whole-Wheat or Sourdough Bread | These breads have a lower glycemic index and more fiber, leading to a more gradual rise in blood sugar compared to refined white flour. |
| Potato Chips or Pretzels | A Handful of Almonds or Walnuts | Nuts are rich in healthy fats, fiber, and protein. This combination stabilizes blood sugar and provides sustained energy without the carb crash. |
| Fruit Juice | A Whole Piece of Fruit (Apple, Pear, Orange) | The fiber in whole fruit is crucial. It slows sugar absorption, whereas juice delivers a concentrated dose of sugar straight to your bloodstream. |
These small changes might not seem like much on their own, but when you make them consistently, they add up to a significant positive impact on your blood sugar levels.
How does pairing foods help control blood sugar?
Here's another powerful technique I always recommend: never let a carb go out alone. Eating carbohydrates by themselves, especially refined ones, is a recipe for a quick glucose spike. But when you pair those carbs with protein and healthy fats, you completely change the metabolic math.
Protein and fat digest much more slowly than carbohydrates. When you eat them together, they effectively put the brakes on the whole digestive process, which blunts the glucose response from the carbs and helps you feel full and satisfied for much longer.
Think about your morning oatmeal. By itself, it can still cause a decent blood sugar rise. But if you stir in a spoonful of chia seeds (for fiber and healthy fat) and top it with a handful of almonds (for protein and fat), you’ve just transformed it into a blood-sugar-stabilizing powerhouse.
Why is fiber so important for blood sugar?
Fiber truly is a superstar for metabolic health. It’s a type of non-digestible carbohydrate, and both of its forms play a huge role in keeping your blood sugar in check.
- Soluble Fiber: This type dissolves in water and creates a gel-like substance in your digestive tract. This gel slows down glucose absorption and can even help lower cholesterol. You'll find it in foods like oats, beans, apples, and carrots.
- Insoluble Fiber: This is the "roughage" that doesn't dissolve. It adds bulk to your stool, which promotes regularity and keeps your digestive system moving. It's abundant in leafy greens, nuts, and whole grains.
Making sure your diet is rich in both types of fiber is one of the most fundamental things you can do to keep your blood sugar levels steady all day long.
I know making these shifts can feel like a lot to juggle at first. If you need a hand putting these principles into a structured weekly menu, exploring a dedicated low-carb meal plan can take all the guesswork out of it. An AI Meal Planner can take these concepts and automatically build delicious, balanced menus, making healthy eating feel effortless.
How does exercise impact your glucose levels?
When it comes to managing blood sugar, movement is one of the most powerful tools you have. I like to think of muscles as hungry little sponges for glucose. When you exercise, they soak up sugar right from your bloodstream to use as fuel, and they can do this with much less insulin than they normally need.
This is a huge advantage, especially if you're dealing with insulin resistance. It’s like opening up a VIP lane for glucose to exit your blood and get put to work immediately, helping to bring your numbers down fast.
And the best part? You don't need to sign up for grueling, hour-long gym sessions to see a real difference. The goal here is consistency, not intensity. It's about making movement a natural part of your daily rhythm, not another chore on your to-do list.
What kind of movement is most effective?
Different types of exercise offer unique perks for blood sugar control, and honestly, the magic really happens when you combine them. Think of it as a one-two punch for improving how your body handles sugar.
Aerobic Exercise This is your classic cardio—things like brisk walking, cycling, swimming, or even dancing around your living room. These activities are fantastic for improving your overall insulin sensitivity. Over time, this means your body's cells get much better at responding to insulin, so you don't need as much of it to get the job done. Regular aerobic exercise trains your body to be more efficient at managing glucose around the clock, not just while you're moving.
Resistance Training Lifting weights, using resistance bands, or doing bodyweight exercises like squats and push-ups helps build lean muscle. This is absolutely crucial, because muscle is your body's number one glucose user. The more muscle mass you have, the more "storage space" you have for glucose to go instead of hanging around in your bloodstream.
One of the simplest and most effective habits I recommend is taking a 10–15 minute walk right after your biggest meal of the day. Research has shown this small action can dramatically blunt the blood sugar spike that follows a meal, because your muscles start using that incoming glucose immediately.
How do I build a strong and stable foundation?
When you combine aerobic exercise with resistance training, you get the best of both worlds. The cardio makes your cells more receptive to insulin, and the strength work builds more "storage tanks" for glucose in your muscles. It's a dual-action approach that creates a much more resilient metabolic system.
Of course, to build that valuable, glucose-hungry muscle from your resistance training, you need to be eating enough protein. Adequate protein is non-negotiable for muscle repair and growth. If you're looking for structured ideas on how to hit your protein targets, exploring a high-protein meal plan can give you the nutritional framework to perfectly complement your fitness efforts.
Ultimately, the best exercise is the one you’ll actually stick with. Find something you genuinely enjoy, whether it’s hiking, gardening, or playing a sport. The key is simply to break up long periods of sitting and weave more movement into the fabric of your day.
Why do sleep and stress affect blood sugar so much?
It's a frustrating but common experience: you have a terrible night's sleep and wake up to find your blood sugar has shot up, almost as if you'd eaten a donut. This isn't a coincidence. It's a clear sign of the deep, often overlooked connection between your lifestyle and your metabolic health.
When it comes to blood sugar, think of sleep and stress as two sides of the same coin. Both have a powerful influence over your hormones, which in turn dictate your glucose levels.

The main player here is cortisol, famously known as the "stress hormone." When you're sleep-deprived or stressed out, your body's internal alarm system goes off, flooding your system with cortisol to prepare you for a perceived threat.
To generate a quick burst of energy, cortisol signals your liver to dump stored glucose into your bloodstream. At the same time, it makes your cells more resistant to insulin. This creates a perfect storm for high blood sugar—you have more sugar circulating and less ability to get it into your cells.
How does sleep deprivation disrupt your system?
Skimping on the recommended 7–9 hours of sleep a night does more than just make you groggy; it throws your entire hormonal system out of balance. Even a single night of poor sleep can significantly decrease your insulin sensitivity.
This means your body has to work harder, producing more insulin to do the same job, which puts a major strain on your pancreas.
But it doesn't stop there. This hormonal chaos messes with your appetite, too. Lack of sleep cranks up ghrelin (the "I'm hungry" hormone) and dials down leptin (the "I'm full" hormone). The result? Intense cravings for high-carb, sugary foods—the very things that send blood sugar on a wild rollercoaster ride.
Key Takeaway: Prioritizing sleep is not a luxury; it's a fundamental strategy for blood sugar management. Protecting your sleep is just as crucial as watching your diet or exercising.
How can I build a better sleep routine?
Improving your "sleep hygiene" can have a profound and direct impact on your metabolic health. The goal is to create a consistent, relaxing routine that tells your body it's time to power down.
- Stick to a Schedule: Try to go to bed and wake up around the same time every day, even on weekends. This is the single best way to regulate your body's internal clock, or circadian rhythm.
- Create a Wind-Down Ritual: An hour before you plan to sleep, start winding down. Dim the lights and put away the screens. Instead, read a physical book, sip some herbal tea, or listen to calming music.
- Optimize Your Environment: Your bedroom should be a cave—cool, dark, and quiet. If you have light pollution or noise, consider blackout curtains or a white noise machine.
How can I tame the effects of daily stress?
Let's face it, modern life is stressful. The constant pressure from work, family, or finances can keep cortisol levels elevated all day long. This state of chronic stress creates a constant internal battle that makes glucose regulation incredibly difficult.
Managing this stress is non-negotiable if you want to lower your blood sugar naturally.
You don't need to meditate for an hour to see benefits. Simple mindfulness and relaxation techniques can effectively lower cortisol. Even a few minutes can make a world of difference.
Try this simple breathing exercise right now: inhale slowly through your nose for a count of four, hold your breath for four, and then exhale slowly through your mouth for six. Repeating this simple cycle for just two minutes can calm your nervous system and help reset your stress response.
Which supplements and herbs can actually help lower blood sugar?
While your daily habits with food and exercise are the unshakeable foundation of blood sugar control, a few specific supplements and herbs have some promising science behind them. Think of these as helpers, not magic bullets. They can offer an extra layer of support, but they’re most effective when they’re backing up an already solid routine.
It’s also critical to remember that “natural” doesn’t automatically mean “safe for everyone.” Many herbs and supplements can interact with prescription medications or might not be a good fit for people with certain health conditions.
Important: Always talk to your healthcare provider before adding any new supplement to your routine. They can help you figure out if it’s the right choice for you, determine a safe dosage, and make sure it won’t interfere with your current treatment plan.
What are some evidence-backed options for support?
Walking down the supplement aisle can be overwhelming, with countless bottles all making big claims. But a few options consistently stand out in the research for their role in metabolic health. These aren't shortcuts, but they can be valuable additions to a comprehensive plan to lower your blood sugar naturally.
- Berberine: This plant compound has been getting a lot of attention, and for good reason. Some studies suggest its effects on blood sugar can be comparable to certain pharmaceutical drugs. It works by activating an enzyme called AMPK, which helps your body improve insulin sensitivity and get glucose into your cells more efficiently.
- American Ginseng: A staple in traditional medicine, American ginseng has been shown in studies to improve fasting blood glucose levels. Some people find that taking it before a meal helps blunt the blood sugar spike that follows.
- Cinnamon: More than just a tasty spice for your oatmeal, cinnamon—specifically Ceylon cinnamon—may help your cells become more sensitive to insulin. This makes it easier for glucose to move out of your bloodstream and into your cells where it belongs.
Does Moringa help with blood sugar?
One particularly interesting plant is Moringa oleifera, a nutrient-packed tree with a long history in traditional remedies for managing diabetes. Modern clinical data is now starting to back up this ancient wisdom, showing some pretty remarkable blood sugar-lowering effects.
For instance, one pilot study found that Moringa leaf powder significantly reduced post-meal blood glucose in people with diabetes.
Animal studies have shown even more dramatic results, with extracts from the plant causing rapid drops in both blood and urine sugar. These findings highlight the potential for certain botanicals to powerfully influence how our bodies manage glucose. You can dig deeper into the research on Moringa's effects on blood sugar to see the data for yourself.
How can I choose and use supplements safely?
If you and your doctor decide a supplement is a good option for you, quality is everything. The supplement industry isn't as tightly regulated as the pharmaceutical world, so you have to be a savvy consumer.
Look for products that have been third-party tested by organizations like NSF International, USP, or ConsumerLab. This certification acts as a stamp of approval, verifying that the product actually contains what the label says it does and is free from harmful junk.
Remember, the goal here is to complement all the hard work you're putting in with your diet and fitness. These are simply tools in your toolbox, supporting the positive changes you're making every day to take control of your health.
When should I talk to a doctor about my blood sugar?
While natural strategies are a fantastic first line of defense, it’s critical to understand their limits and know when professional medical advice is non-negotiable. Think of lifestyle changes as a powerful way to support your body—not replace the guidance of a doctor, especially if you're already managing a condition like diabetes or prediabetes.
This journey is a partnership between you and your healthcare team. While some supplements have shown real promise, they need to be handled with care and professional oversight.
For instance, studies on American ginseng have shown clear benefits for people with type 2 diabetes. A daily intake of just 3 grams (split as 1 gram per meal) was found to lower fasting blood glucose, HbA1c, and even systolic blood pressure. You can dive deeper into the ginseng study findings here.
What warning signs should I watch for?
Even with your best efforts, certain symptoms are red flags that mean it's time to call your doctor. Pay close attention to these specific signs, as they could indicate that your blood sugar levels are in a dangerous range.
Signs of Hyperglycemia (High Blood Sugar):
- Extreme thirst that you just can't seem to quench
- Needing to urinate frequently, especially waking up at night to go
- Unexplained, persistent fatigue or a feeling of lethargy
- Blurred vision that seems to come and go
Signs of Hypoglycemia (Low Blood Sugar):
- Feeling shaky, dizzy, or lightheaded
- Sweating, chills, or clamminess
- Confusion or finding it hard to concentrate
- A rapid or pounding heartbeat
These symptoms, particularly the ones for hypoglycemia, can require immediate medical attention. Never hesitate to reach out to a professional if you experience anything severe or concerning. Your safety always, always comes first.
Frequently Asked Questions
How fast can you lower blood sugar naturally? You can lower blood sugar immediately with a short walk after a meal. More stable, long-term improvements in blood sugar readings can often be seen within one to three months of consistent diet and lifestyle changes.
What is the best drink to lower blood sugar? Water is the best drink to lower blood sugar. Staying hydrated helps your kidneys flush excess glucose from your system and prevents the concentration of sugar in your bloodstream that occurs with dehydration.
Can I lower my A1c in 3 months? Yes, it is possible to significantly lower your A1c in three months with consistent diet, exercise, and lifestyle modifications. The A1c test reflects your average blood sugar over the previous two to three months.
What is a natural blood sugar blocker? Fiber-rich foods like beans, oats, and avocados act as natural blood sugar blockers. The soluble fiber in these foods slows down digestion and the absorption of sugar into the bloodstream, preventing sharp spikes.
Does lemon water lower blood sugar? While lemon water helps with hydration, which is beneficial for blood sugar control, there is no strong scientific evidence that the lemon itself has a significant direct effect on lowering blood sugar levels.
How can I flush sugar out of my system fast? The fastest way to help flush sugar out is by drinking plenty of water and engaging in light physical activity, like walking. Exercise helps your muscles use the excess glucose for energy, and water helps your kidneys excrete it.
What vitamin deficiency causes high blood sugar? Low levels of Vitamin D and magnesium have been linked to impaired insulin function and higher blood sugar. Ensuring adequate levels through diet or supplements may help support better glucose management.
Ready to take the guesswork out of healthy eating? The AI Meal Planner creates personalized meal plans and smart grocery lists tailored to your health goals, making it effortless to eat delicious, blood-sugar-friendly meals every day. Start your journey to better health today.
AI-powered nutrition
Get Your Personalized Meal Plan
AI creates the perfect meals for your goals, lifestyle, and taste.
Start Your Journej



